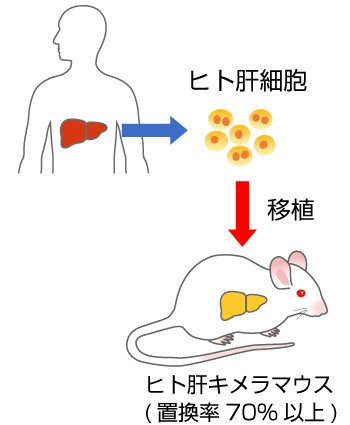
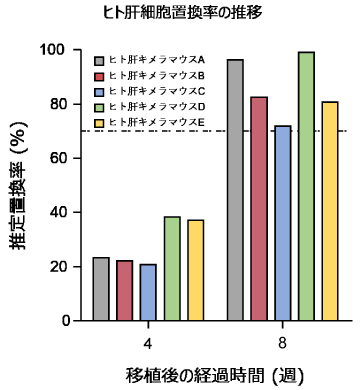- 肝臓の70%以上がヒト肝細胞に置換されたマウス。
- 肝臓にヒトの薬物代謝酵素やトランスポーターが発現します。
- 薬物動態研究や肝炎ウイルス研究に利用されます。
- 肝臓から単離したヒト肝細胞をin vitro薬物動態・安全性評価へ利用できます。
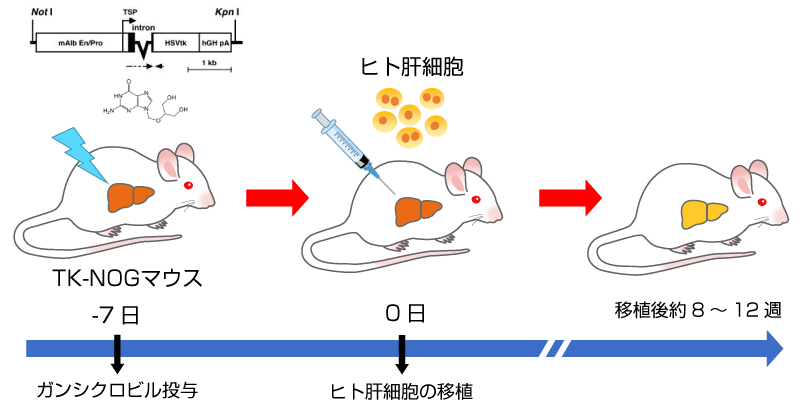
ヒト肝キメラマウスの作製手順
- TK-NOGマウス*にガンシクロビルを投与し、肝傷害を誘導します。
- 血漿ALT活性を目安に肝傷害の程度を確認し、ヒト肝細胞を脾臓経由で移植します。
- 血漿中のヒトアルブミン濃度を指標に肝臓におけるヒト肝細胞の置換率を推定します。
*肝臓にウイルス由来チミジンキナーゼ(TK)を発現するNOGマウス. ガンシクロビルを投与すると肝臓のTKによりDNA合成阻害物質であるガンシクロビル三リン酸が生成され肝傷害が誘導されます。
血漿中ヒトアルブミン濃度によるヒト肝細胞置換率の推定
- 血漿中ヒトアルブミン濃度を指標にして肝臓におけるヒト肝細胞の置換率を推定します。
- 移植後約8-12週で肝臓におけるヒト肝細胞の割合が70%以上に達します。
肝組織におけるHLAおよびCYP3A4の発現分布
ヒト肝キメラマウス肝臓の大部分がヒト肝細胞(HLA陽性細胞)に置換されます。
ヒト肝キメラマウス肝臓のCYP3A4の発現分布はヒト肝臓と類似しています。(中心静脈周囲に局在)
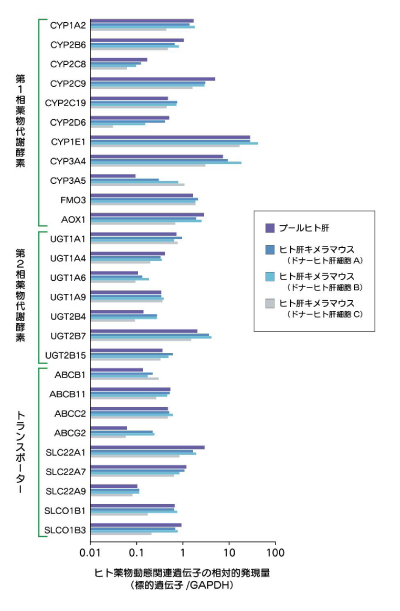
ヒト肝キメラマウス肝臓におけるヒト薬物動態関連遺伝子の発現量
ヒト肝キメラマウス肝臓では、ヒト薬物動態関連遺伝子がヒト肝臓と類似したレベルで発現しています。
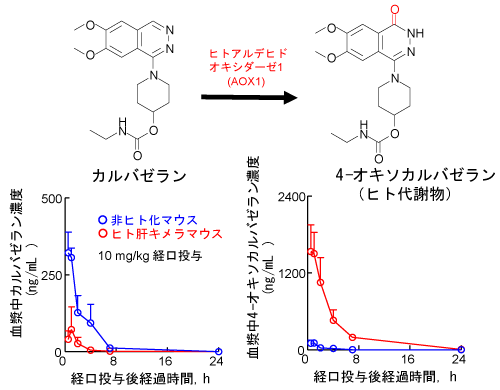
In vivo薬物投与実験によるヒト代謝物生成の予測
- マウス肝AOX酵素活性は低いため、カルバゼラン投与後のマウス血漿に検出される4-オキソカルバゼランは僅かです。一方、ヒト肝キメラマウスでは肝臓のヒトAOX1によりカルバゼランが速やかに代謝され、血漿中に4-オキソカルバゼランとその誘導体が豊富に検出できます。
- ヒト肝キメラマウスはヒトにおけるAOX依存的な薬物代謝を再現できるモデルであることが示唆されました。
ヒト肝キメラマウスの主な用途
- ヒトにおける主要代謝経路および排泄経路の同定
- ヒト循環血中の代謝物の予測
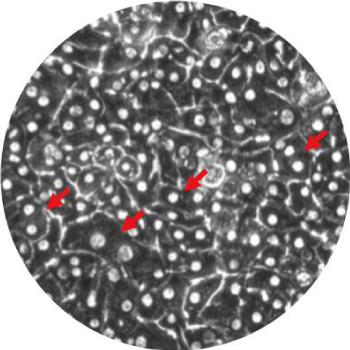
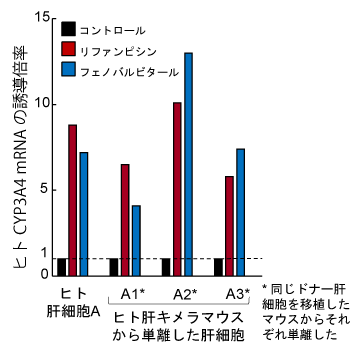
ヒト肝キメラマウスから単離した肝細胞の特徴
- ヒト初代培養肝細胞に認められる多角形状で多核(矢印)の細胞形態を保持しています。
- 典型的なヒトP450誘導剤によるCYP1A2, CYP2B6,およびCYP3A4の酵素誘導が認められます。
- 代謝クリアランス、酵素誘導などの薬物動態評価およびマラリア原虫の感染実験に使用できます。
文献集
-
Drug transporter expression and activity in cryopreserved human hepatocytes isolated from chimeric TK-NOG mice with humanized livers.
Zerdoug A et al. Toxicol In Vitro. 2023 Aug;90:105592.
-
HepaSH cells: Experimental human hepatocytes with lesser inter-individual variation and more sustainable availability than primary human hepatocytes.
Uehara S et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Jun 30;663:132-141.
-
Roles of human cytochrome P450 3A4/5 in dexamethasone 6beta-hydroxylation mediated by liver microsomes and humanized liver in chimeric mice metabolically suppressed with azamulin.
Uehara S et al. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2023 Jun;50:100504.
-
o-Toluidine metabolism and effects in the urinary bladder of humanized-liver mice.
Yokota Y et al. Toxicology. 2023 Apr;488:153483.
-
The Unique Human N10-Glucuronidated Metabolite Formation from Olanzapine in Chimeric NOG-TKm30 Mice with Humanized Livers.
Uehara S et al. Drug Metab Dispos. 2023 Apr;51(4)480-491.
-
Different Hepatic Concentrations of Bromobenzene, 1,2-Dibromobenzene, and 1,4-Dibromobenzene in Humanized-Liver Mice Predicted Using Simplified Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models as Putative Markers of Toxicological Potential.
Miura T et al. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020 Dec 21;33(12):3048-3053.
-
Human plasma concentration-time profiles of troglitazone and troglitazone sulfate simulated by in vivo experiments with chimeric mice with humanized livers and semi-physiological pharmacokinetic modeling.
Ito S et al. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020 Dec;35(6):505-514.
-
Comparative Transcriptomics Analyses in Livers of Mice, Humans, and Humanized Mice Define Human-Specific Gene Networks.
Jiang C et al. Cells. 2020 Nov 30;9(12):2566.
-
Predicted values for human total clearance of a variety of typical compounds with differently humanized-liver mouse plasma data.
Nakayama K et al. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020 Aug;35(4):389-396.
-
Prediction of circulating human metabolites of pemafibrate, a novel antidyslipidemic drug, using chimeric mice with humanized liver.
Ogawa SI et al. Xenobiotica. 2020 Jul;50(7):769-775.
-
Human Aldehyde Oxidase 1-Mediated Carbazeran Oxidation in Chimeric TK-NOG Mice Transplanted with Human Hepatocytes.
Uehara S et al. Drug Metab Dispos. 2020 Jul;48(7):580-586.
-
A novel Css-MRTpo approach to simulate oral plasma concentration-time profiles of the partial glucokinase activator PF-04937319 and its disproportionate N-demethylated metabolite in humans using chimeric mice with humanized livers.
Kamimura H et al. Xenobiotica. 2020 Jul;50(7):761-768.
-
Metabolism of desloratadine by chimeric TK-NOG mice transplanted with human hepatocytes.
Uehara S et al. Xenobiotica. 2020 Jun;50(6):733-740.
-
Different Roles of Human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and 3A Enzymes in Diclofenac 4'- and 5-Hydroxylations Mediated by Metabolically Inactivated Human Hepatocytes in Previously Transplanted Chimeric Mice.
Miura T et al. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020 Feb 17;33(2):634-639.
-
Hepatitis C virus infection suppresses hepatitis B virus replication via the RIG-I-like helicase pathway.
Murai K et al. Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 22;10(1):941.
-
Expansion, in vivo-ex vivo cycling, and genetic manipulation of primary human hepatocytes.
Michailidis E et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 21;117(3):1678-1688.
-
In vivo functional analysis of non-conserved human lncRNAs associated with cardiometabolic traits.
Ruan X et al. Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 2;11(1):45.
代表的な実験動物